Why AI technology can play a huge role in community energy management?
Introduction
Tracing back to the origins of humankind, it seems that we have been tagged as social animals, we are used to living in a settlement, we are used to the unique atmosphere formed by a small group, which we call life. From the earliest primitive settlements to the current residential communities, different types and functions have been derived to meet the diverse needs of residents. With the continuous development of AI technology, people are no longer satisfied with the concept stage of research, intelligent, sustainable and human-centred design is becoming the key target of the new generation of communities, the concept of the future community gradually into reality.
Definition
Future Community refers to a new model of community governance that enhances community autonomy, public participation and local social interaction through digital technology. It emphasises the application of innovative technologies, but also focuses on humanistic care and ecological protection, and is dedicated to creating a more humane and sustainable community life. The goal of Future Community is to improve the quality of life of community residents and enhance community cohesion through digital technology.(Manley, A., Shen, D., Clift, B., Ma, Y. and Zhang, W,2024)
AI technology changing the way energy is managed
In Energy Management, AI is promoting intelligent upgrading of community energy systems using smart grid, distributed energy management and energy saving and optimisation technologies. For example, by establishing a smart residential community strategy which aims to promote the efficient use of renewable energy and reduce the cost of electricity consumption for residents. Residents are allowed to exchange energy with neighbouring energy storage devices, leading to low-cost consumption of renewable energy.(Conte, F., D’Antoni, F., Natrella, G. and Merone, M,2022)
AI can also use machine learning algorithms to analyse the community’s historical energy consumption data and user behaviour patterns to predict energy demand and optimise energy allocation. For example, by combining AI and Model Predictive Control (MPC) to effectively manage energy in a Renewable Energy Community (REC). The approach uses Time Delay Neural Networks (TDNN) to predict three key energy characteristics in RECs, namely solar photovoltaic power generation, overall energy consumption and public services, with the aim of reducing energy wastage.(Mahmoud, M. and Ben Slama Sami ,2023)
In smart home, AI monitors the energy consumption of home appliances in real time through IoT technology, displays it on the user’s client and automatically adjusts air conditioning, lighting and other equipment to achieve reduced energy consumption to reduce carbon emissions.
Precedent Study
Google Downtown West
Google Downtown West is a smart community invested by Google in San Jose, California, USA, aiming to create a technology-driven sustainable city of the future. The project covers about 80 acres and is planned to house 20,000 residents and can rely entirely on renewable energy.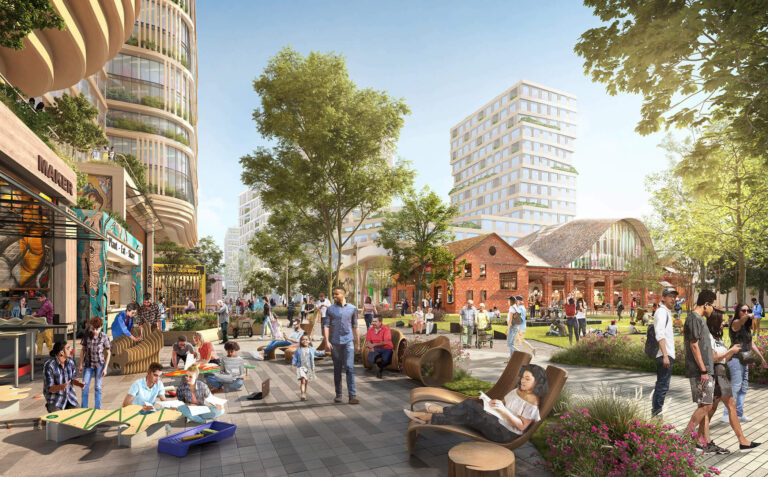
Figure1-Google Downtown West(Grimshaw Architects,2025)
By managing the grid through AI and integrating it with renewable energy sources, the community is powered by 100 % renewable energy, using algorithms to predict solar and wind power generation and automatically adjusting the energy storage system to ensure the stability of the power supply, which is expected to increase the community’s power self-sufficiency rate to 80 %.
Figure2-Google Downtown West(Grimshaw Architects,2025)
In addition, the community uses AI to manage the energy consumption of all buildings in the community, including residences, office buildings and shops. Combined with an IoT application, residents can view the energy consumption of their homes in real time and get energy-saving advice. Through smart building management, the community is expected to be able to 35 % of its energy consumption, which significantly reduces energy costs for residents and businesses.
Songdo, Korea
Located in Incheon, South Korea, the Songdo International Buissness District is an over $35 billion investment in efficient energy management and low carbon development through the use of AI algorithms, big data, IoT and other technologies.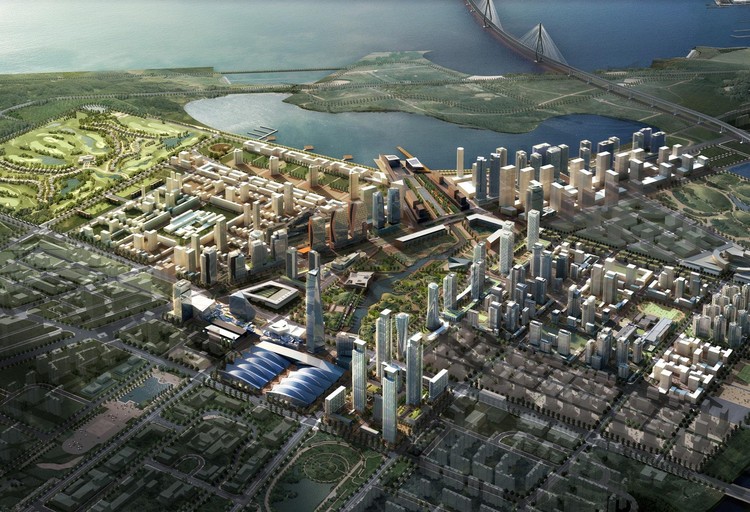
Figure3-Image Courtesy of Songdo, Korea(The Story of Songdo, Korea,2021)
Songdo International Buissness District aims to be one of the greenest and smartest cities in the world, and in order to achieve these ambitious goals, the city has been built using some of the world’s leading technologies. The roads connecting the areas are fitted with sensors to monitor energy consumption and traffic conditions as a way of quantifying sustainability for the world’s highest density of LEED-certified projects that the city has to offer.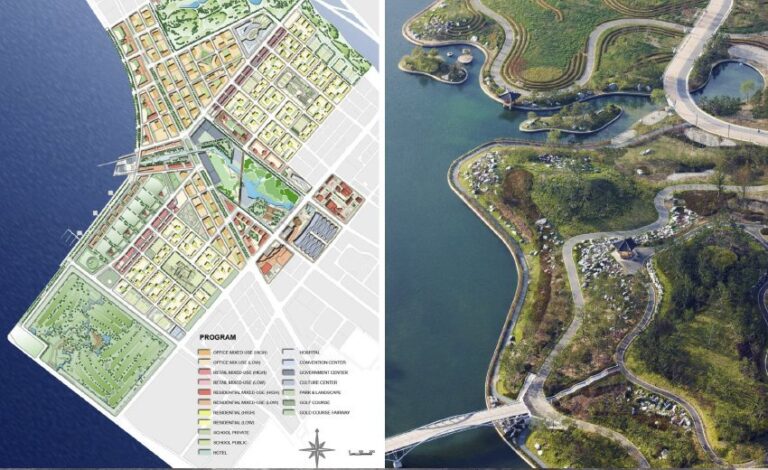
Figure4-Masterplan of Songdo, Korea(The Story of Songdo, Korea,2025)
Songdo also boasts a giant waterfront park, complete with a self-sufficient irrigation system that provides plenty of public space. As far as individual residents are concerned, a waste pipeline transports household waste to a central processing plant, where it is automatically sorted for recycling or incineration. Even residential homes can be controlled via a mobile app, from heating and cooling to lighting brightness.Songdo’s AI-driven energy management has resulted in a reduction in overall energy consumption of more than 30 % and a 40 % reduction in carbon emissions.(Overstreet, K. 2021)
Conclusion
The cases of Google and Songdo show that AI is comprehensively affecting the community’s energy management model, through smart grids, renewable energy optimisation, and intelligent building management systems, which can achieve the purpose of optimising energy scheduling and reducing carbon emissions. In the future, with the advancement of AI technology, there will be more and more smart technologies applied in the future community to bring convenience to the residents. AI technology can improve community energy management, enhance public safety, improve traffic flow, and provide residents with more convenient and personalised services. From smart security systems to autonomous driving, from smart home systems to unmanned delivery services, AI is playing the role of the ‘community brain’, and is driving the transformation of the urban management paradigm.
Reference:
- Manley, A., Shen, D., Clift, B., Ma, Y. and Zhang, W. (2024). A new direction for neighbourhood governance and community construction in China: the case of Zhejiang province’s ‘Future Communities’. Space and Polity, pp.1–22. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/13562576.2024.2388320.
- Conte, F., D’Antoni, F., Natrella, G. and Merone, M. (2022). A new hybrid AI optimal management method for renewable energy communities. Energy and AI, 10, p.100197. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyai.2022.100197.
- Mahmoud, M. and Ben Slama Sami (2023). Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading Case Study Using an AI-Powered Community Energy Management System. Applied sciences, 13(13), pp.7838–7838. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137838.
Image reference:
- Grimshaw Architects (2025). Google Downtown West / GRIMSHAW. [online] Grimshaw.global. Available at: https://grimshaw.global/projects/workplace/google-downtown-west/ [Accessed 16 Mar. 2025].
- Overstreet, K. (2021). Building a City from Scratch: The Story of Songdo, Korea. [online] ArchDaily. Available at: https://www.archdaily.com/962924/building-a-city-from-scratch-the-story-of-songdo-korea?ad_source=search&ad_medium=projects_tab&ad_source=search&ad_medium=search_result_all.


