Energy, Heat and Cooling in Housing Architecture (research record)
Thermal Performance and Energy of Buildings
The thermal adjustment of buildings is divided into active thermal control and passive thermal control. This allows us to ensure that we live in a comfortable indoor environment. These keep us from gaining too many calories or losing too many calories. But with the impact of global warming and climate change, the need for building carbon emissions and sustainability requirements has become an imminent issue. (Roger Greeno&Guildford, cited in Fred Hall 2012)
Before we talk about heat control, we need to talk about something that everyone knows, the form of heat conduction.
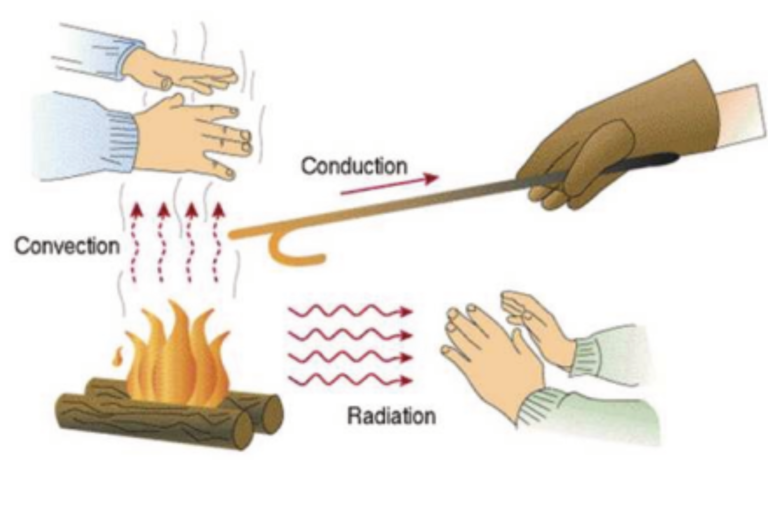
The way heat spreads affects how we will control its spread.
The following is my own summary of thermal control in buildings.
Passive Thermal Control
Residential building in the UK is mainly based on thermal insulation.
Insulation
• Material
• prevent air convection
• reflect heat radiation
Structural insulation (such as temporal bridge)
• Insulation of structural joints
• window insulation
Active Thermal Control
In areas with significant temperature difference between the four seasons (such as 38 degrees in summer, but -2 degress in winter)
Air conditioner system:
Heat&cooling exchange system
• Central air conditioning
Fresh air system
• Windows system
• Ventilator
Max:
• Mechanical Ventilation with Heat Recovery (MVHR)
In areas with little temperature difference between four seasons (such as 24 degrees in summer, and 3 degress in winter)
Heating system:
• Electric Water Heaters
• Gas Water Heaters
• Hot Water Storage Capacity
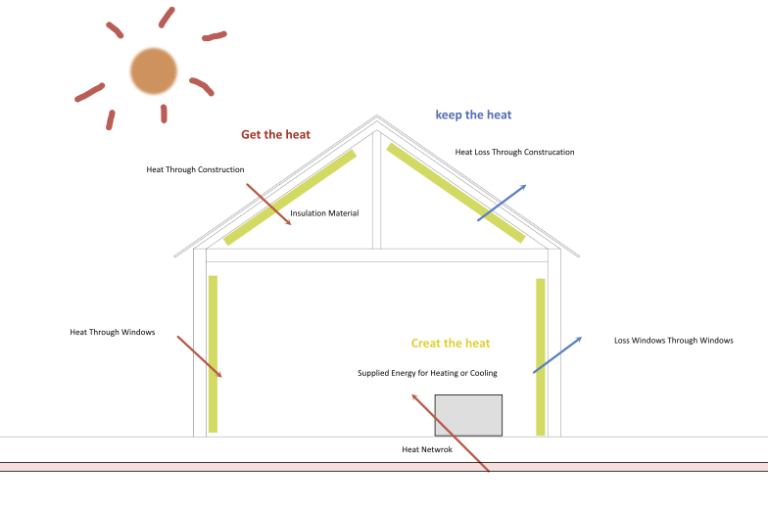
Simply put, it is the means of insulation and building cooling & heating facilities.
Passive Thermal Control
Thermal Insulated Materials
Bulk Insulation – Conductive and convective insulators
Reflective Insulation – Radiant barrier


by Ing. Klára Vokáč Machalická, Ph.D. form01_thermal resistance

Different materials have different thermodynamic properties and fire performance, and some materials have gradually integrated their sound insulation and heat preservation functions. (Patnaik, A., Mvubu, M., Muniyasamy, S., Botha, A. and Anandjiwala, R.D. 2015.)
Structural insulation
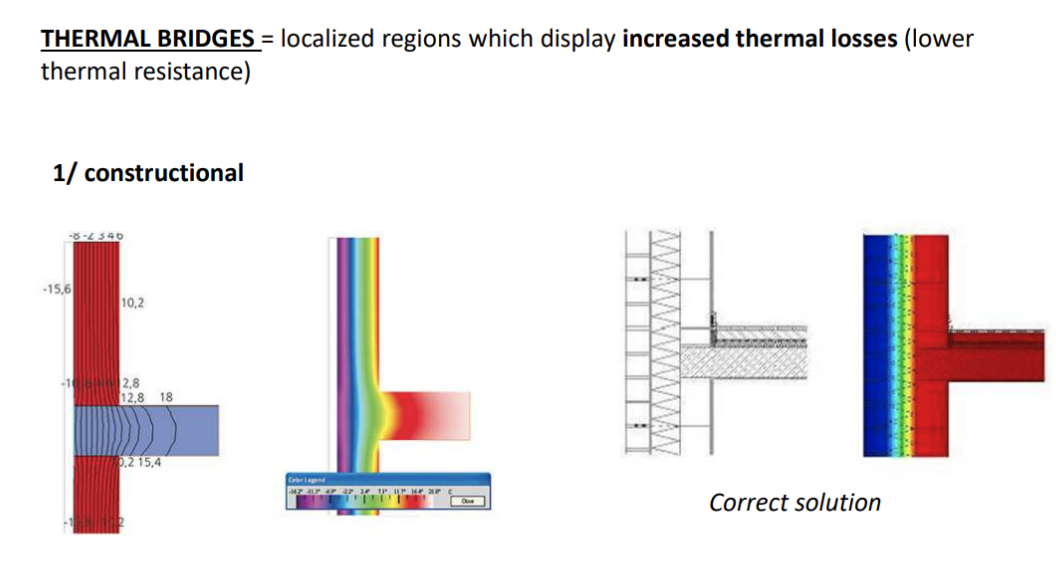
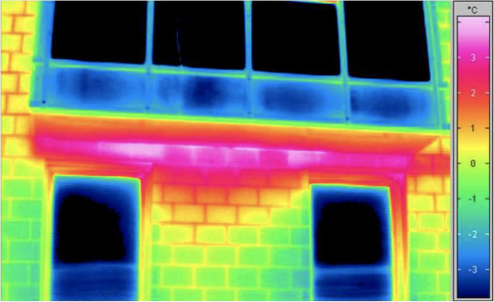
The heat conduction between structural parts will also affect the thermal insulation performance of the building, which needs to be designed in advance to avoid it. The following are some cases after thermal bridge formation.
Active Thermal Control
The Heaters

electric immersion heater cistern-type heater Instantaneous water heaters
Gas Water Heaters
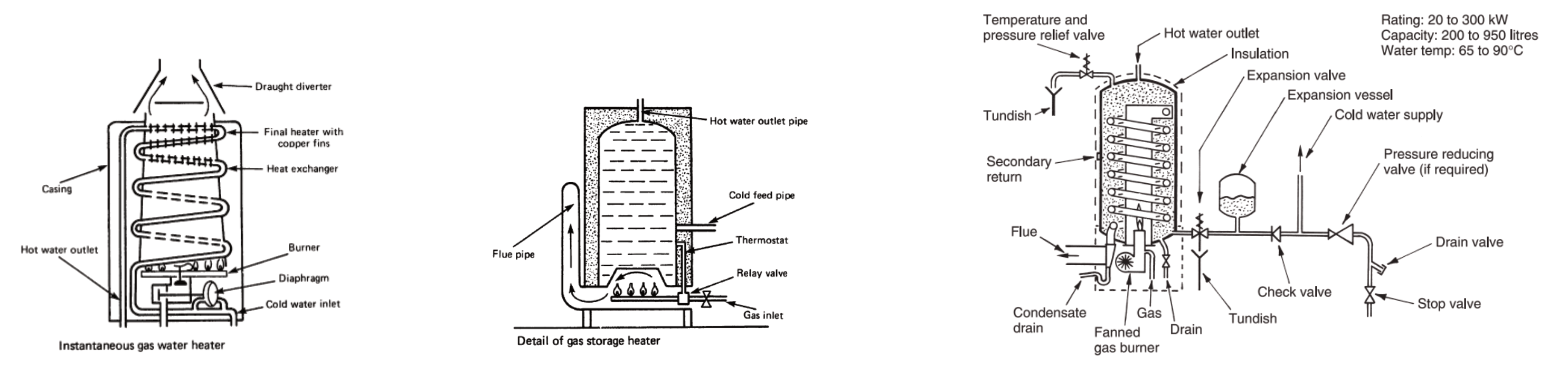
Instantaneous gas water heater storage type of gas water heater Condensing water heater – a variation on the multipoint type heater
Active Thermal Control
Solar Heating
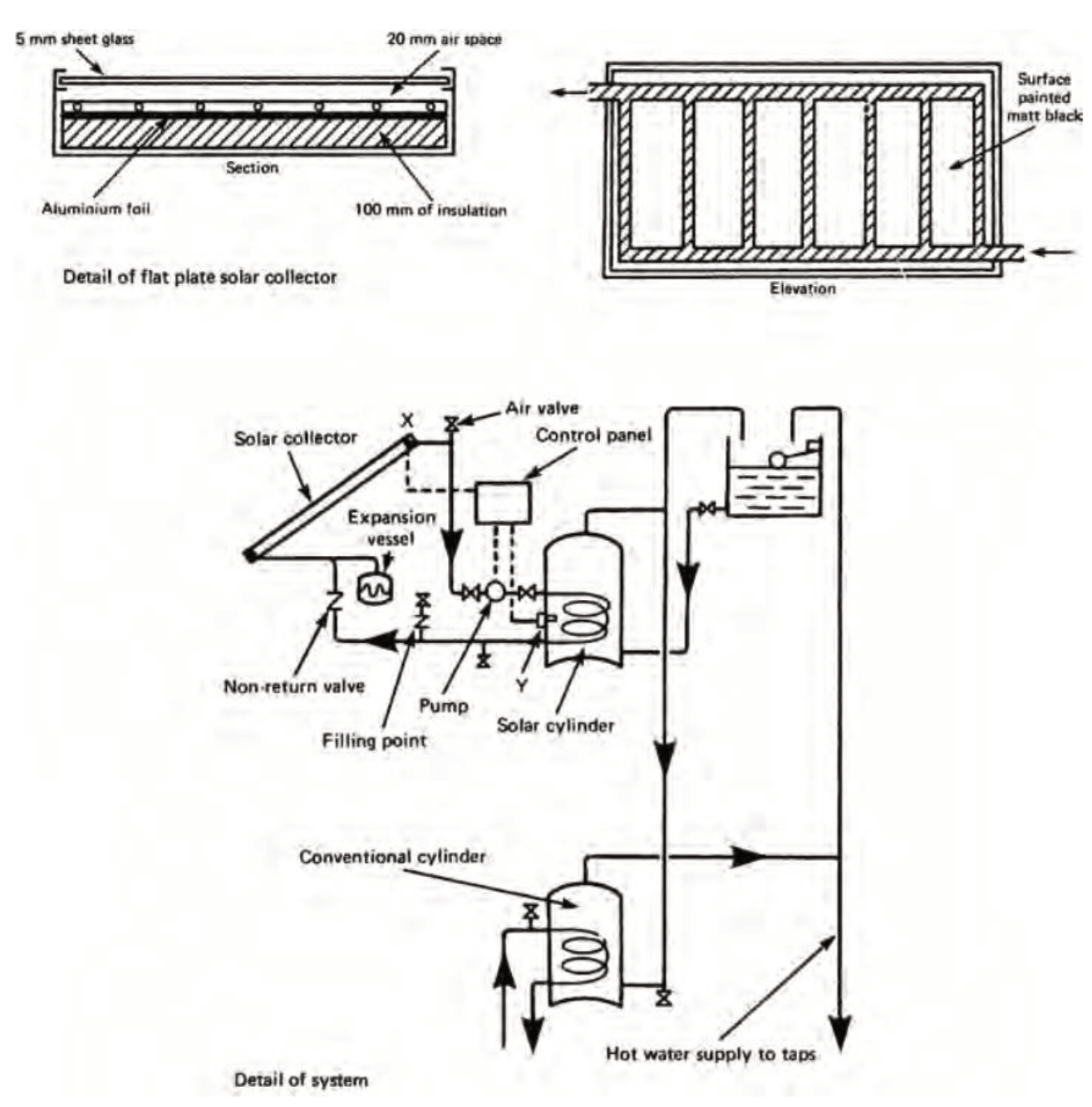
Solar Heating of Water
Heat pump

Air conditioner
Thermal Performance and Energy of Buildings
Heat network
Save energy by connecting it.



