housing construction in severe cold regions
Despite the differences in geographical conditions, economic development, culture, social systems and lifestyles of individual countries, the resource and energy issues faced by each country are consistent in the development of enhancing and improving the performance of the built environment.
Housing needs to be structured in a way that is not only sustainable, but also appropriate to the local climate and environment in a variety of ways.When building sheltered housing in harsh cold regions, grasp the housing needs of low-income groups under natural conditions, understand housing performance, reasonably control costs,To improve the durability of building components during the life cycle of a building, to reduce waste emissions, to reduce energy consumption, to reuse building components that have been dismantled or have changed in function and performance, and to reuse envelope components that require special consideration in terms of insulation and freeze protection.
The potential for energy efficiency in building envelopes in cold regions is huge, and in cold regions, where temperatures are low and heating costs are high, building energy efficiency is very important.The building envelope is an important component of building energy efficiency, including walls, roofs, windows and doors.In cold regions, optimising the design of the building envelope can greatly reduce energy consumption, lower heating costs and improve the comfort of the building. Energy saving measures for the envelope include.
1.Wall insulation
Wall insulation is one of the most important measures for building energy efficiency, which can effectively cut off or reduce the cold bridge of the wall and improve the thermal stability of the room under non-stable heating conditions.The addition of insulation layers on the surface of external walls, such as polystyrene, polyurethane and rock wool panels, which have excellent thermal insulation and durability, can effectively reduce the energy consumption of buildings, improve the thermal insulation performance of walls and reduce the loss of heat.
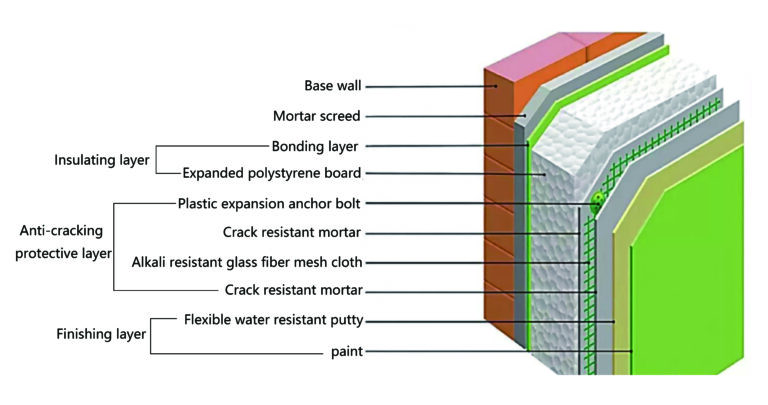
Photo credits:Wall insulation – Bing images
2. Window and door insulation
The thermal insulation performance of doors and windows is very important because it is most likely to break in buildings. While using multi-layer glass, you need to choose doors and windows with good thermal insulation performance: for example, aluminium alloy, PVC, wood composite materials, etc. with good thermal insulation performance and durability to prevent heat consumption.

Photo credits:Door and window insulation – Bing images
3.Frost-proof drainage
In cold regions, where drainage systems are susceptible to freezing, frost-proof taps and pipes are essential for outdoor plumbing to prevent breakage in cold conditions.For indoor water pipes, heating measures can be applied by installing heating tape around the pipes to ensure that the temperature of the pipes does not fall below 0°C.On top of the heating tape, the insulation can be wrapped to improve the insulation and reduce energy consumption.And, the use of hot water circulation systems can be used. In buildings, hot water circulation systems are used to deliver heat through the hot water pipes to the pipes that need to be heated to achieve the heating effect.
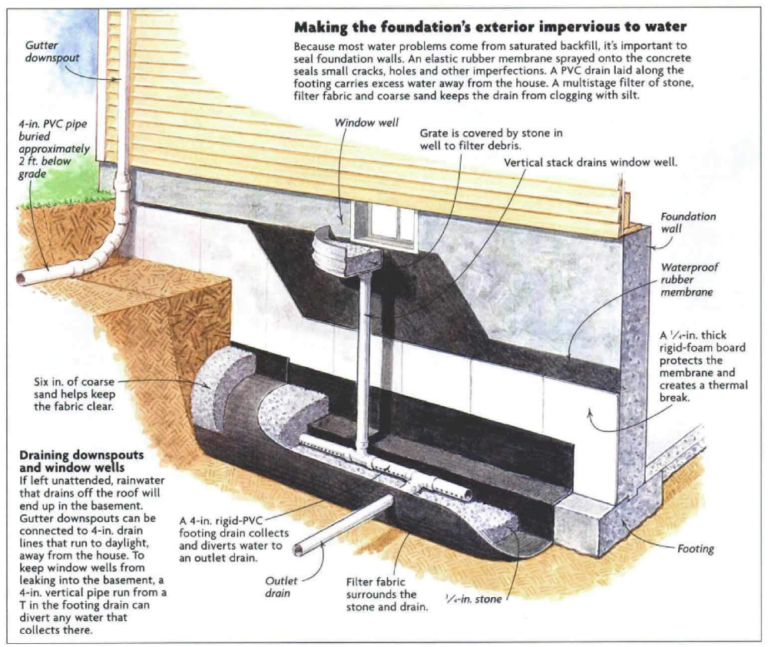
Photo credit:Foundation Drainage System – Bing – Bing images
4.Seismic resistance
Consideration needs to be given to the condition of the foundations, which are the foundation of the building.The stability and seismic resistance of foundations have an important impact, reducing the impact on buildings in earthquakes and reducing the temperature changes in the soil to mitigate the effects of freeze-thaw phenomena on foundations.You can choose polystyrene, polyurethane foam, cement foam insulation board, glass fibre insulation wool, all of which have a long service life, are not easily affected by moisture, and can effectively reduce the impact of freezing and thawing of the ground on the foundation and play a role in earthquake resistance.

Photo credit:Seismic Resistance of FOUNDATIONS – Bing – Bing images
5.Green
In cold regions, where there is a lot of wind and snow, it is a technical measure to use the environment around the building to plant trees and flowers appropriately, not only for aesthetic purposes, but also to improve the microclimate of the regional environment, which is also a technical measure to save energy in the building. Trees should be planted to avoid direct sunlight in the summer, which will lower the ambient temperature and improve the local microclimate; in winter, after the leaves have fallen, the sunlight can shine into the room and increase the indoor temperature, which will have a positive effect on building energy efficiency.
Photo credit:Planting of trees in severe cold regions – Bing images
Reference:
Smith, P.F., 2009. Building for a changing climate: the challenge for construction, planning and energy. Earthscan.
Greeno, R., 2004. Building Construction Handbook: Incorporating Current Building & Construction Regulations. Taylor & Francis.
Hall, J.M., Handley, J.F. and Ennos, A.R., 2012. The potential of tree planting to climate-proof high density residential areas in Manchester, UK. Landscape and Urban Planning, 104(3-4), pp.410-417.
Li Hongyan .Sheltered Housing in Severe Cold Areas Architectural design study 2014.06
Wang Liying. Hao Qiushi. Characteristics of residential building culture and wall insulation system in severe cold regions [J]. Changchun Engineering Journal of Changchun University of Engineering, 2008
Zhang Xian Yao. Research on the modular construction and evaluation of green building technology system.2012.08


